Static First Development Approach
King's Digital Lab, King's College London
Introduction
- Traditional web development often relies on complex, resource-intensive stacks (e.g., Django)
- Moving towards a more sustainable, low-resource approach using static site generators (SSGs)
- Benefits: improved performance, security, scalability, and reduced hosting costs
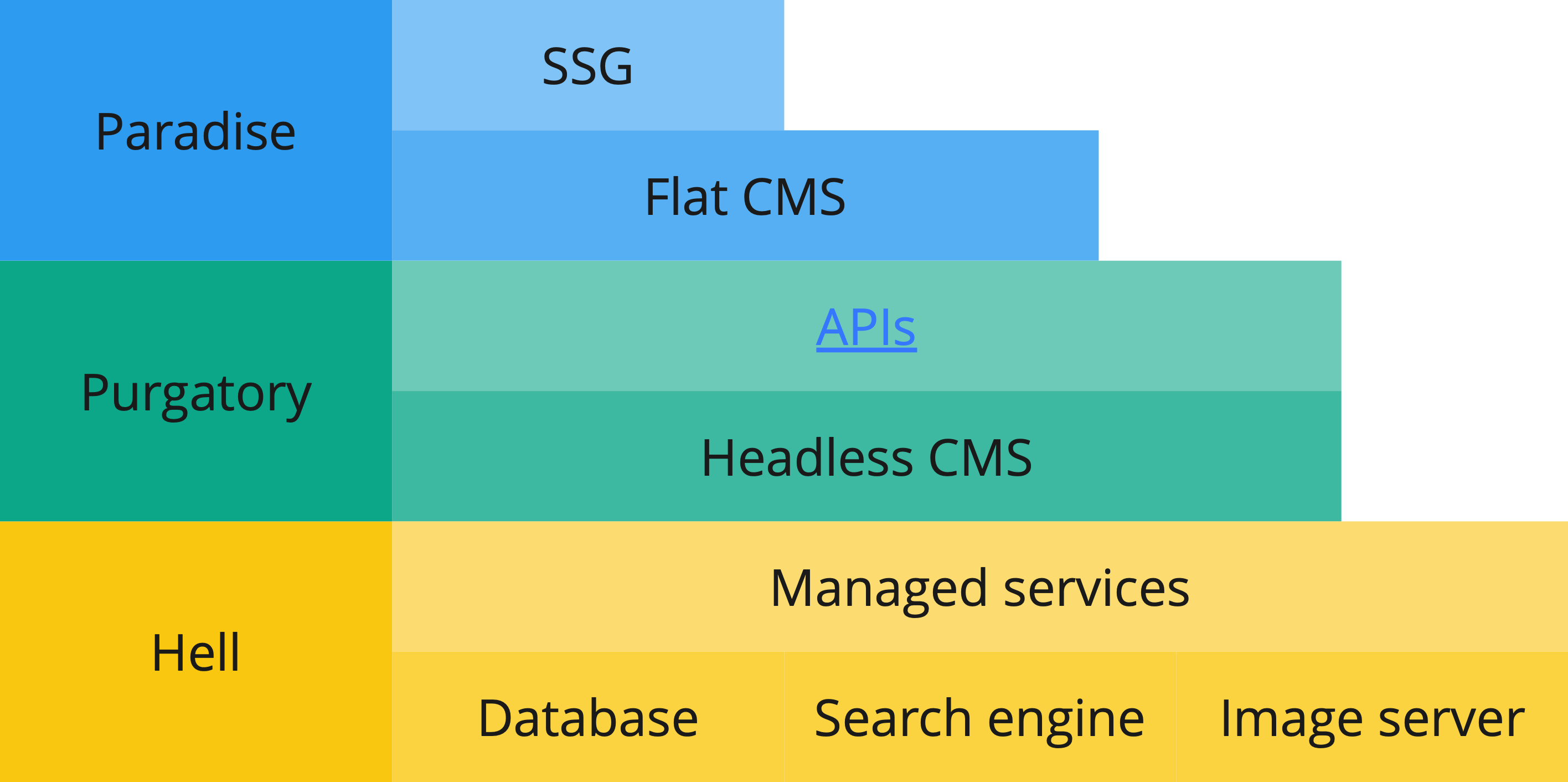
The Static First Development Approach
- A modular, flexible approach for building websites and web applications
- Follows a technical stack with at most 3 components:
- Static Site Generator (SSG) as the base
- Flat File CMS (optional)
- Headless CMS (optional, for more complex projects)
The Static First Development Approach
Component 1: Static Site Generator
- Generates static HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files from templates and data sources
- Examples: 11ty, Jekyll,
Next.js, SvelteKit (static export)
- Benefits: fast performance, secure, scalable, and easy to host
Component 1: Static Site Generator
Component 2: Flat File CMS (optional)
- Provides a user-friendly interface for managing content in flat files (e.g., Markdown)
- Examples: Front Matter, Decap CMS
- Suitable for smaller, content-driven projects
Component 2: Flat File CMS (optional)
Component 3: Headless CMS (optional)
- Decoupled content management system, serving content via APIs/data exports
- Examples: Directus, Pocketbase
- Suitable for projects that require advanced content modeling and dynamic content delivery
Component 3: Headless CMS (optional)

Using Standard Data Models
- Adopt standard data models based on schema.org
- Enables content portability and interoperability
- Aligns with semantic web principles
- Examples: Article, Event, Person, etc.
The Stack Migration Process
- Previously used a Django-based stack (monolithic)
- Recently introduced Docker for improved containerization and scalability
- Now moving towards a static first approach for sustainability reasons
Benefits of the Static First Approach
- Improved performance and scalability
- Enhanced security (reduced attack surface)
- Lower hosting and maintenance costs
- Better developer experience (simpler tooling, faster build times)
- Easier deployment and content updates
Challenges and Considerations
- Limited real-time interactivity (can be mitigated with JS frameworks)
- Potential content modeling limitations (depends on CMS choice)
- Learning curve for new tooling and workflows
Conclusion
- The static first approach offers a sustainable, low-resource solution
- Modular stack allows flexibility and scalability
- Suitable for a wide range of projects, from simple websites to complex web applications
- Based on the JAMstack (JavaScript, APIs, and Markup) architecture




